Business plan for a winter greenhouse. Winter greenhouses and their production Winter greenhouses for a private home
Whatever they say about the variety of greenhouses, in fact, there are only two types: capital and non-capital. All others are varieties. Greenhouses also differ in their design: wall-mounted, covered with wood, large arched type and small arched type.
A winter greenhouse is not just a place for planting vegetables and flowers, but also an indicator of the skill of a gardener. Organizing and equipping a winter greenhouse is a very difficult process, requiring knowledge, special skills and training.
Types of winter greenhouses
- Capital type of greenhouse must be built with a foundation. A trench is installed in the center, a deep passage necessary for accumulating cold air, preventing it from reaching the roots of plants. The design of the greenhouse allows it to warm up quickly, which makes it possible to plant seedlings 2-3 weeks earlier.
- Conditional capital ( non-capital) the type of greenhouse makes it easy to dismantle and move the structure to any other place. To manufacture this type, polycarbonate, metal profiles, and bolted connections are used. The basis is piles. In all other respects, the entire structure is similar to the capital one, but without thermal insulation and a central trench.
All other types of greenhouses are transitional options. But only in a permanent greenhouse it is possible to organize both lighting and heating.
Winter greenhouses differ according to the following parameters:
- By functionality. You can grow not only traditional vegetables, but also exotic crops. Before building a greenhouse, it is important to decide what crops will be grown. The entire process of arranging a greenhouse, external and internal, depends on this.
- By location to the ground. All heated greenhouses are divided into 3 main types: deep into the ground, made on the surface, equipped on the top of the building (barn, garage, etc.)
- By architectural decision. Among the existing options for greenhouses, single-, double-, triple-sloped, arched, wall-mounted, and combined ones stand out.
Choosing the right option
Choice the appropriate option depends entirely on taste and financial capabilities; the size of the greenhouse will also be important. Greenhouses also differ:
- By type of building materials. For the manufacture of greenhouses, brick, wooden materials, metal or PVC frames are used. Glass and polycarbonate coatings are also often used. Combined designs are very popular.
- By heating type. There are solar greenhouses, biofuel greenhouses, greenhouses with technical heating (stove, gas, electric, water).
- For planting. Plants in a greenhouse are planted directly into the ground or into special containers placed on racks.
Choosing a location for a greenhouse
When choosing a location for a future greenhouse, 2 main factors are taken into account:
- Lighting. For normal growth and development of plants, good lighting is necessary. If there is insufficient lighting, it will be impossible to grow light-loving crops (tomatoes, peppers, cucumbers). The best place to equip a winter greenhouse will be a lengthwise location from west to east. This point is especially important when constructing a solar greenhouse.
- Wind direction. If cold winds prevail in the area, then protection of the greenhouse will be required. With proper organization, you can significantly save on heating. Access to the greenhouse should be wide and convenient. This is necessary for construction and subsequent operation.
In the presence of fencing an important factor to consider. The fence should not be close to the greenhouse to avoid turbulence from wind currents. If the height of the greenhouse is 2.5 m, then the distance between the greenhouse and the fence should be at least 7-8 m. The most ideal option would be a distance of 15-20 m.
Construction of a gable in-depth greenhouse
This is the most universal a greenhouse that is suitable for both mid-latitudes of Russia and more severe climates. In greenhouses of this type, you can easily grow vegetable, horticultural, and exotic crops. A gable greenhouse is convenient and has a long service life. The construction is reliable and economical.
Gable The greenhouse consists of 2 rooms: a vestibule and a greenhouse.
The vestibule serves as a workroom where the heating system (boiler) is installed, and if all greenhouse maintenance processes are automated (watering, lighting, ventilation), then so is the control unit. The area of the vestibule should be at least 1.5 m (optimally 2−2.5 m).
Also vestibule used for preparing earthen mixture, for storing garden tools, etc. Brick is used for the construction of the vestibule. For thermal insulation, the best material would be polystyrene foam or mineral wool. The vestibule roof is covered with an opaque material such as corrugated sheeting, roofing iron, etc.
Partition between the vestibule and the greenhouse it is made permanent. The material can be a plastic or metal-plastic profile.
When building an in-depth greenhouse structure, the main rule should be observed - the soil is selected to a depth of 80 - 90 cm (depth of the freezing layer). This rule is also used for the foundation of non-deep greenhouses.
- Foundation. On dense soil, the foundation is poured to a depth of 45 - 50 cm.
- Walls. When building walls in a greenhouse, one brick masonry is used (the wall thickness should be 25 cm).
- Window for installation of frames, they are located at a height of 50 - 60 cm above ground level. The width between the windows should be 50 - 75 cm or 2 -3 bricks. This will provide the plants with additional lighting. Ventilation transoms are required.
- Roof. The gable roof shape is one of the most convenient. It ensures unhindered water flow. Tilt angle 20 -25 degrees.
To equip the roof, the lower trim beams are laid on the side walls. Then the tracing beam is attached to the strapping beams using rafters.
Materials required for the roof:
- Strapping beams and ridge beam (section 120×150 mm);
- Rafter-beam (section 70×100 mm).
To ensure free penetration of light for the roof, 4 mm thick glass is traditionally used. The roof glazing is carried out using grooves (40×75 mm) with gutters for condensate drainage.
One of the most popular roofing materials today is polycarbonate honeycomb. If you compare it with glass, then glass is very inferior in many respects. A polycarbonate greenhouse will last at least 15 years. This is a warm and safe room.
The glass is laid from the lower framing beam, moving upward. For putty, compositions based on drying oil or plastic mixtures are used. To protect the walls from water leakage, a canopy is installed. The distance of the canopy from the wall is 6-8 cm.
Heating
 Choice heating for a greenhouse depends entirely on the size of the room. For greenhouses with an area of 15−20 sq. Stove heating is also suitable. But for heating large greenhouses, the following options exist: electric, biofuel, water heating.
Choice heating for a greenhouse depends entirely on the size of the room. For greenhouses with an area of 15−20 sq. Stove heating is also suitable. But for heating large greenhouses, the following options exist: electric, biofuel, water heating.
With the system water Heating uses a water heating boiler, pipes and a tank. The pipes are placed either directly into the ground (at a depth of 40 cm), or from above, under the racks.
Electrical heating is divided into 3 types: cable, air and infrared heating. The cable room is equipped like a heated floor. Air is provided using fan heaters. IR heating is produced by infrared heating devices placed under the ceiling.
Heating biofuel is the most economical type of heating. The soil and air warm up as heat is released during the decomposition of organic matter. Among the most used biomaterials are:
- Horse manure - maintains a temperature of 33-38 degrees for 70-90 days;
- Cow dung - 20 degrees 100 days;
- Rotten bark - 25 degrees 120 days;
- Sawdust - 20 degrees 2 weeks;
- Straw - 45 degrees for 10 days.
Biofuel placed in the ground, under the fertile layer. When using biofuels, you need to remember about the acidity level, it affects the quality of the land. Cow manure has the most optimal level (6−7 pH). Bark and sawdust create acidic environment, horse dung - alkaline. Biofuel after consumption can be used as humus.
If all technical standards were observed during the construction of the greenhouse, then it will delight you with good harvests for many years.
At first glance, the organization of year-round greenhouse farming does not differ from seasonal vegetable growing. It seems that it is enough to install a stove in a standard greenhouse, and we can consider that we have built a winter greenhouse with our own hands. However, experienced greenhouse growers warn that it is impossible to grow certain crops in winter without proper preparation for the construction of closed soil. What are the differences between a greenhouse that is fully functioning in the cold season and what algorithm should be followed in order to competently build a reliable shelter?
Features of winter greenhouses
If you intend to get a high-quality harvest at any time of the year, it is not enough to build a greenhouse, even from polycarbonate - take the example of industrial complexes. We are not talking about size, although they are also important, but about the internal arrangement. The use of units that are almost irrelevant for summer structures, but extremely important for winter ones, allows one to avoid many problems that usually nullify all the efforts of amateur vegetable growers.
Reliable shelter for winter harvests
The difference between winter greenhouses and summer ones
The construction of a winter greenhouse in modern agricultural complexes involves the installation of high-tech equipment that performs the following tasks:
- space heating and cooling;
- additional lighting and shading of plants;
- humidification, support of air exchange and soil irrigation;
- fertilizing with fertilizers and carbon dioxide;
- disinfection and treatment against pathogens;
- monitoring of microclimate and planting condition.

Greenhouse equipment
Full automation of an all-season greenhouse is beyond the capabilities of the average summer resident, and he must be prepared to carry out most of the processes independently. However, there are some problems that are extremely difficult to resolve manually. This:
- insufficient sealing and thin walls compared to the permanent structure cause high heat loss and exorbitant monthly heating costs;
- due to the reduction in daylight hours, plants do not receive the required amount of light, grow poorly, get sick and bear unmarketable fruits;
- in the cold season, natural ventilation leads to a sharp cooling of the air, and the high cost of energy resources needed for heating forces us to limit the use of this method of ventilation.

Insulation of a greenhouse structure
Thus, the design of a polycarbonate winter greenhouse must include a heating system, as well as ventilation and lighting equipment. In addition, it is necessary to take measures to insulate the building and minimize heat loss by choosing the optimal design.
Main types of winter greenhouses
Unlike seasonal greenhouses, warm greenhouses, especially in northern regions with low levels of insolation, are almost independent of the source of natural light. That is why you can see winter structures of protected ground, almost completely or half hidden underground - the so-called thermos greenhouses.
In addition to thermoses, the following types of structures have proven themselves well in year-round use:
- arched (tunnel) under a double layer of film;
- single-slope house with a common power supply system;
- insulated gable roof with polycarbonate covering.

The principle of an underground greenhouse
The main advantage of using trench greenhouses is savings on technical heating and guaranteed protection against sudden temperature changes. Since the soil temperature at a depth of two meters is practically unchanged throughout the year, heat is well stored in the structure - at –25 °C and the boiler is turned off, a positive temperature within 3 °C is maintained inside.
However, an underground greenhouse in winter, and sometimes in summer, needs to be additionally illuminated, and for ventilation it must be equipped with a system of supply and exhaust fans. As a result, energy costs increase so much that building a complex and expensive trench greenhouse becomes unprofitable.

Greenhouse-trench
Film winter greenhouses are good for their versatility. On the eve of the onset of frost, they can be insulated without much difficulty, and with the arrival of warmth, they can be quickly opened. However, the problems of ordinary summer greenhouses are not alien to them - the film must be changed as it wears out (and it breaks much faster in the cold), installation is inconvenient, and besides, single film shelters are only suitable for the southern regions.
As for single- and double-slope polycarbonate greenhouses, these are the most popular solutions among amateur vegetable growers. They are built with their own hands everywhere - and this despite the high cost of components. The main reason is reliability and ease of construction. Although in the case of a winter structure, this simplicity is deceptive, and before starting construction, carefully calculate the project on paper for specific conditions.

Heated design
How to create a project
If you take the matter seriously, it is better to order the design from professionals - they will prepare a full package of technical documentation, accurately calculate the construction estimate and thereby save you from force majeure situations and unforeseen expenses.
It is also possible to independently draw up a plan for setting up a greenhouse for growing vegetables in winter. The “Manual for the design of greenhouses and greenhouses” (attached to SNiP 2.10.04-85), which contains calculation examples, will help you with this:
- foundation,
- frame,
- heat shields,
- snow protection, etc.

Arched frame
Of course, in the manual you will not find a method for calculating a winter greenhouse made of polycarbonate - in those days, honeycomb sheets were just being introduced into experimental greenhouse plants. However, there are online and offline computer programs that will help you roughly determine:
- usable area of the structure;
- full area of glazing of the roof, walls and facades;
- the total length of the frame materials.
To obtain this and other data, set the input conditions:
- design shape - rectangular or semicircular;
- width, height and length of the greenhouse;
- number of wall and roof sections.

Greenhouse project for a summer residence
Determine the dimensions of the structure based on the following factors:
- for what purposes (personal consumption, sale, type of crops, in what quantity) do you want to build a winter greenhouse with your own hands;
- what is the area and shape of the existing land plot, where it is located;
- is it possible to add a technical room;
- how many people are ready to work and in what mode;
- What are the possibilities of the family budget?

Ground heating system diagram
The next crucial moment in drawing up a project for a year-round greenhouse is the calculation of heating, for which you first need to determine the level of energy consumption using a simplified scheme (you will find it in the book by V.V. Klimov, “Equipment of greenhouses for subsidiary and private farms”). Now calculate the heat capacity of the carrier and the total amount of thermal energy, and then, taking into account the type of most accessible fuel, select the type and power of the boiler.
Technology for constructing a winter greenhouse step by step
The correct design of a greenhouse is considered to be one that provides the plantings with a warm and humid microclimate regardless of any weather changes. Therefore, before building a winter greenhouse, carefully read the step-by-step algorithm based on the principles of energy saving and compliance with building codes.
Choosing a location on the site
Any structure for year-round use (with the exception of a thermos greenhouse) should be as open as possible from the south and protected from the north. Guided by this rule, inspect the plan of your site and determine the area where it is observed. The ideal option is if you can attach a greenhouse to the southern facade of a heated structure, for example, to a house. However, this is not always possible.

Greenhouse extension
It is possible that the southern site is well lit, but at the same time completely open to the north wind. To prevent a self-built greenhouse from losing excess heat in winter, equip it with a protective screen (monolithic fencing, gazebo) and/or insulate the northern wall as much as possible. Here are a few more theses, the implementation of which can significantly reduce heat losses in the future:
- there should be no monumental buildings or plantings near the structure - they threaten not only with shading of the greenhouse, but also with the collapse of snow or ice on its surface;
- It is highly undesirable to install a free-standing greenhouse on a hill or hill;
- The natural slope of the site is permissible only to the south, otherwise some of the plants will not receive enough sunlight.

Site layout
Please note that the construction of greenhouses is subject to the requirements of land legislation specified in SNiP 30-02-97 “Planning and development of territories of gardening associations of citizens, buildings and structures.” According to it, it is recommended to install the greenhouse structure at a distance:
- at least 5 m from the red line of the street and driveway;
- 3 m from the border with the neighboring plot;
- 15 m to any wooden building if the greenhouse frame is made of wood.
For the sake of ease of use of the site, it is advisable to install the greenhouse in a gardening area, including a vegetable garden, garden, greenhouse, garden house, etc.
Preparation of materials
As an example, consider the stages of building a year-round greenhouse with an asymmetrical shape with your own hands. According to the project, it is insulated on the northern side, and equipped with transoms on the southern side for ventilation. In order to maximize the use of sunlight, the northern wall is covered with reflective material on the inside. Outside, the entire greenhouse is covered with polycarbonate or, as an economical option, with a double layer of film.
For such a design you need to stock up on the following building materials:
- metal profiled pipes 60x40 (frame racks) and 40x25 (supports) with a wall thickness of 2 mm;
- cement, sand, crushed stone and reinforcement (for arranging the foundation);
- foil thermal insulation and polycarbonate (or two types of polyethylene film: for the first layer - from frost-resistant polyethylene, for the second - from air bubble);
- polystyrene foam for insulating a cold, light-proof wall;
- clamping cables for fastening the covering.

Greenhouse structure under film
Select the quantity and parameters of materials based on the area of the future greenhouse, snow and wind loads characteristic of your region. Film coating is not ideal, but it will last for 2-3 years, and then you can install polycarbonate. In this way, many beginning greenhouse growers reduce the initial costs of very expensive construction.
If you plan to make a greenhouse frame from wood with your own hands, be sure to prepare it:
- make sure that the wood is well dried - remove the shavings with a plane and crush them in your hands (dry material crumbles, but wet material crumples);
- if necessary, dry the timber - use professional drying or stack the lumber under a canopy, leaving a gap of 2-3 mm between each beam;
- treat the wood with an antiseptic that prevents rot, by immersing it in a solution or spraying it from a spray bottle.

The result of saving on polycarbonate
And remember, in winter the greenhouse will be subject to numerous loads, so you should not skimp on the quality of components.
Selecting the type of heating
How to build a winter greenhouse with heating with your own hands so that it is efficient and inexpensive? To answer this question, first check out all the possible options:
- biological heating - its organization requires organic matter, for example, horse manure, the decomposition of which leads to intense heat release;
- electric heating - heat is produced by electrical appliances (convectors, cables, heat guns, pumps, etc.) equipped with heating elements;
- gas systems - provide for the installation of a gas boiler and pipe layout, thanks to which thermal energy is distributed throughout the entire volume of the greenhouse;
- heating with solid and liquid fuels - this is provided by installing a homemade or purchased stove that runs on coal, wood, pellets or waste oil.

Soil heating
To decide on the type of heating for winter, think about what type of energy is most available in your region - gas, wood, coal or electricity. Also consider the pros and cons inherent in each type of heating system:
- the use of biofuel leads to a rapid but short-term increase in heat in the room, so this option is not suitable for winter greenhouses;
- the high cost of electricity nullifies the main advantages of its use (ease of installation and operation). However, electricity can be used for heating in an emergency;
- gas still remains the cheapest energy carrier, but to connect it, a project and its approval by the regulatory service are required, and the greenhouse itself must be located in close proximity to the gas main.

Stove heating
Thus, for most greenhouse farms, the most acceptable way to arrange a heating system is to use solid fuel equipment. Its cost varies widely, maintenance is quite simple, and the necessary supply of firewood can be made in advance.
Construction of a greenhouse step by step
To make the winter greenhouse solid, mark out the area for the foundation. To reduce the cost and simplify construction, you can use not a strip base, but columnar concrete supports into which the racks will be walled up. The distance between them is 1 m, the diameter of the supports is 180 mm in the upper part and 250 mm in the lower part. Each of them is reinforced with three reinforcement rods with a diameter of 10 mm.

Holes (borks) for arranging a point foundation

Concrete supports
The next stage of construction is the installation of a frame consisting of a northern and southern part. His algorithm looks like this:
- Use a pipe bender to bend the pipes to the desired radius.
- Install center posts on the north side.
- Tie them together with the top strap.
- Weld bent pipes to the harness on one side and the other.
- Install and weld the side parts of the frame.

The central pillars and the southern part of the frame are installed

The northern side has been installed, insulation has begun
Now insulate the structure from the north. To do this, cover the north wall with reflective insulation from the inside, and install foam sheets on the outside in two layers 5 cm thick. Cover the outside of the foam with a layer of greenhouse film 150 microns thick. Attach the top to a beam or strip of plywood pre-attached to the frame, and press the bottom down with earth.
All that remains is to paint and cover the finished frame from the south and at the ends with a solid sheet of film or polycarbonate. Remember that plastic panels must be installed with edges along the frame racks. It is recommended to fasten them with self-tapping screws equipped with thermal washers with rubber gaskets. To stabilize the microclimate, place a second layer of air bubble film under the first layer of shelter.
Important! The film is not suitable for regions with snowy winters and for buildings with stove heating!
When the structure is ready, proceed with the installation:
- subsoil heating pipes;
- ground heating registers;
- drip irrigation.
Attach the heating registers to the supply and return pipes through flexible connections on heat-resistant washers, and install a ball control valve on the reverse side.
Video: building a winter greenhouse at the dacha
As you can see, the principle of constructing a winter greenhouse with your own hands is quite different from constructing a conventional greenhouse. Loads that have increased several times (snow, wind), sudden temperature changes, and a minimal amount of natural light require compensation by installing:
- reinforced frame and cover made of polycarbonate,
- high-quality insulation and uninterrupted heating,
- installation of ventilation and lighting equipment.
Considering the high cost of building materials and the instability of the market, be sure to calculate the possible benefits and risks yourself or contact specialists with this question. If you are confident in your own abilities, find out from the video additional subtleties of the project and start implementing it.
Video 1: Winter greenhouse-vegetarian made of polycarbonate
Video 2: Gas heating
Video 3: Artificial lighting with LED and HPS lamps
Currently, amateur gardeners strive to please themselves and their loved ones with vegetables and fruits all year round. A winter greenhouse is perfect for this. In addition, it can become not just a tool for a summer resident’s harvest or a gardener’s flower hobby, but also an excellent source for business (depending on the design and desires of its owner).


Peculiarities
Nowadays, it’s rare to surprise anyone with a greenhouse on a private plot. Winter greenhouses are a special project that is equipped with everything necessary for growing crops in the cold season.

This is a real find: both for ordinary amateur gardeners and for professional farmers, as well as novice businessmen.
The main advantages of a winter greenhouse are its convenience and capabilities, thanks to which you can enjoy fresh vegetables all year round.
Its main features include a number of characteristics.
- Capitalism. Unlike a regular greenhouse or summer greenhouse built with your own hands, the winter version is more thorough. It will no longer be possible to “roll it up” so easily and move it from place to place. The design of such a greenhouse requires more effort and money. A heavy frame, dense materials, as well as heating and lighting sources will allow you to grow crops all year round.
- Square. For ease of operation of a winter greenhouse, it usually has a large area and considerable height, so that workers can work comfortably in it, and plant crops receive the necessary conditions for a high-quality harvest. Drawings of such structures take into account all the requirements of the owner, and also provide space for various sources and mechanisms for the continuous supply of energy and heat.
- Different zones. Depending on what crops the owner intends to grow, it is worth foreseeing the division into zones in advance. Some crops require more heat, and therefore heating, and some require less. The design of the greenhouse should contain several adjustable zones, as well as the ability to provide additional insulation in case of unforeseen external temperature conditions.



A winter greenhouse will be an excellent tool and source for harvesting during the cold season. As a rule, they are placed on private plots or on the territories of large enterprises. They are equipped with everything necessary for a high-quality harvest, however, there are several types of their designs that are better suited for one or another type and type of operation.
Types: drawings and diagrams
Currently, there are organizations that offer standard designs for winter greenhouses.
Such schemes can be divided into several types.
- Capital. The frame does not require assembly and disassembly of the structure; it is built on a foundation, in the center of which a trench is erected to collect cold air. This is a more reliable option, which, with additional lighting sources, guarantees a high-quality harvest in the cold season. In addition, it is extremely easy to use and does not require additional insulation. Typically used by professional farmers to obtain large quantities of crops.
- Conditional capital. They are usually built on summer cottages. Such a drawing provides for a collapsible frame so that, if necessary, the greenhouse can be disassembled and moved to another location. However, this is not the same as summer greenhouses. Such designs require significantly more effort and time. The foundation is made of piles, and the floor, in most cases, is made of wood.



Drawings of year-round greenhouses can also be divided by type of structure itself.
- Greenhouse thermos. It differs from other options in that the main part of such a greenhouse is underground. Due to this design feature, a “thermos” effect is created, which provides the necessary heat for the successful cultivation of crops. The most popular option for summer residents and gardeners.
- Arched greenhouse. Suitable for those who are more comfortable growing crops in the ground. It is the most difficult to construct, since problems often arise with the installation and construction of the frame, as well as with the cladding. Polycarbonate is used as the main material. Most often, this option is purchased “ready-made” at specialized bases, and then installed on a summer cottage.
- Greenhouse with a gable roof. The best option for both summer residents and farmers. Due to the design feature, there are no problems with the roof sagging, since due to the slope it is actually self-cleaning. Typically used for those who want to grow crops in boxes. It has a high ceiling, making it possible to work in it at full height, which is comfortable for workers.



- Greenhouse with mansard roof. Suitable for doing business. It is usually used for growing flowers, since the design features allow you to place as many tiered racks indoors as possible. A warm atmosphere is usually achieved with stove heating, and transparent walls will provide an additional source of lighting.
- Greenhouse attached to the house. A very convenient option, which is more often used as a winter garden rather than for growing crops. The heated structure receives an additional heat source due to a common wall with the house. In addition, the owner has the opportunity to freely enter the greenhouse by crossing the threshold of his own home, without having to cross the street.


When developing a drawing, it is also worth considering the functionality of the room. It depends on the funds available to the owner, as well as his desires and plans for the greenhouse.

Native and exotic crops require different growing conditions– this also needs to be paid attention to.
The location of the structure in relation to the ground is also important for high-quality heat transfer. The greenhouse can be deep, surface, or part of a heated room (barn, gazebo, house, etc.). Particular attention should be paid to the material from which the structure will be made.




Materials
Conventionally, structures can be divided into:
- wooden;
- metal;
- brick;
- made of polycarbonate;
- glazed;
- made of PVC frame.



However, nowadays conservatory greenhouses are made from two or more combinations of materials. Thus, the design of the product will be much stronger and more multifunctional, as well as more resistant to sudden temperature changes.
The frame is usually made of wood or metal. The first one is cheaper, but is not durable. Options made of steel can withstand significant loads and are more resistant to mechanical damage.




Glass is recommended for use in small greenhouses, winter gardens or greenhouses (since glass is more fragile and weighs more). However, currently they are increasing the stability of the structure with double walls or an additional layer of polycarbonate, which (together) will ensure heat transfer and make the cladding of the room more durable.
When building a winter greenhouse, professionals do not recommend using film as the main means of thermal insulation under the skin, as well as aluminum - due to their fragility and easy exposure to mechanical damage. In addition, condensation can collect under the film, which can freeze if the temperature rises sharply or increase the air humidity inside the greenhouse.

Dimensions
The size of the greenhouse depends entirely on the needs of its owner. For summer cottages, options from 5 to 10 square meters are suitable. m., which has enough space for growing crops for one family. For gardeners, the optimal size for growing flower beds will be 15-20 square meters. m.
To grow crops for sale, large winter greenhouses will be required, which can occupy an impressive area (up to 200 sq. m.) in large enterprises.



How to build?
Currently, there are companies and services that provide their clients with a catalog of various greenhouses, as well as the opportunity to make them to order. You can order the structure, and then do the assembly yourself, or leave it to professionals for an additional fee. However, for many summer residents and gardeners it will not be difficult to make a greenhouse with their own hands.
Before you start, you need to decide in advance on the location for construction. As a rule (depending on the purpose of the greenhouse), the most suitable type of structure is immediately selected and the foundation is laid.


The location itself should be selected taking into account the most optimal protection from the wind. Otherwise, you will have to spend additional effort on protecting the product from gusts of wind, as well as on heating it.
Typically, a winter greenhouse consists of a foundation, frame and glazed roof. The design of the greenhouse must include a ventilation and heating system pre-designated in the drawing to further ensure the favorable functioning of plants. Tightness is of great importance for such a greenhouse, since the temperature in it is maintained artificially.



If the owner plans to grow plants in the ground, then the ceiling of the greenhouse may be low. If you plan to work with shelving, you must ensure in advance that the ceiling height and frame shape are sufficient for comfortable work of workers.

You can start making racks in advance to make sure that they are easy to use even at the construction stage of the building. They are usually made from wooden blocks and boards or plastic.
A winter greenhouse must receive the maximum amount of lighting. In winter, daylight is usually not enough to get a high-quality harvest, so you need to think in advance about installing artificial lighting. It is important that it is not only effective, but also as safe as possible, and also reliably protected from moisture and other conditions that can lead to a short circuit in the system.
The final stage is the arrangement of a homemade greenhouse from the inside. Usually in this case, a specialist is brought in to make sure that all additional systems supporting the life of plant crops are safe. When placing beds, it is worth making wide passages for convenience (taking into account the future dimensions of the plants and their needs).


The finished greenhouse requires careful care in the first year of use. You should be attentive to the occurrence of unwanted cracks, and also take care to maintain tightness, and be careful in operation. It is advisable to be able to insulate the greenhouse from the inside during severe frosts.
How to heat?
The selection of the type of heating for a winter greenhouse must be approached responsibly. It is necessary that it corresponds to the type of structure of the structure, and also meets all safety standards.
For a small greenhouse up to 20 square meters. m. Stove heating will be sufficient. This option is perfect for permanent residents of private houses. Its main advantage is the ability to more finely regulate the temperature inside the greenhouse, due to which you can get a high-quality harvest, and also not depend on abnormal weather temperatures outside.

Biofuel can also be used for such greenhouses. This is the most economical type of heating a greenhouse in winter, but at the same time more time-consuming for the owner. It is laid under the fertile layer of soil and warms the earth through natural decomposition processes.

For larger greenhouses, professionals advise using electric or water heating.
Electrical can be divided into overhead and cable. The air type maintains the necessary favorable temperature conditions for fertile crops inside the greenhouse with the help of special fan heaters.
Cable works like a “warm floor” system, that is, it heats the soil from the inside. It is because of this feature that it is extremely important that it is installed correctly and tested in advance to avoid problems being discovered after the greenhouse has been built.
Water heating is carried out through pipes, which can be installed underground (or through racks).



Growing crops in winter is not an easy task even with a properly equipped winter greenhouse. For a high-quality harvest, it is necessary to use all the advantages of the greenhouse and provide for many nuances in advance (even before the construction stage of this building).
You should follow the operating tips given by professionals to summer residents.
- If you plan to plant such demanding and delicate berries as strawberries in a greenhouse, then you should choose polycarbonate for the cladding of the structure, as well as take care in advance of high-quality artificial lighting and prepare racks in which the seedlings will feel comfortable. Growing berries in the ground is undesirable, as this can lead to the death of plants if there is a strong jump in temperature outside.
- It is better to determine zoning in a greenhouse in advance (before installing the heating system), since cucumbers, carrots, peppers, herbs and other crops require different climatic conditions. By keeping them in advance, you can prepare for a high-quality harvest.
- A greenhouse for growing flowers must include devices for regulating indoor humidity.
- Growing exotic crops requires more effort than traditional plants. That is why the success of selling such a harvest will directly depend on the quality and quantity of all necessary heating and lighting systems. In some cases, it is worth seeking the help of specialists to create the most suitable climatic conditions for certain plants.




A successful harvest depends not so much on the correct arrangement of the greenhouse, but on its competent use by the owner.
Beautiful examples
Design solutions for large winter greenhouses exceed all expectations of private home owners. A winter greenhouse can instantly transform from a place for growing plants into a chic place to relax with a book and a cup of hot tea in your hands. However, one does not exclude the other.
A white frame greenhouse with a high gable roof and glazed windows can become an excellent greenhouse that can accommodate not only small bushes of delicate plants, but also short trees. The brick foundation makes this structure more reliable, and the shape of the roof will not allow the weight of snow to accumulate for a long time. The glazed surface will allow you to enjoy daylight all year round.

A metal greenhouse-“hut” with glass walls will be a wonderful decoration for a winter hunting lodge. Water heating (in addition to the wooden interior) will allow you to enjoy green plants all year round. The sharp shape of the roof combined with the beams makes it extremely resistant to winter weather, as well as another design addition to the backyard.
Winter greenhouses are designed primarily for growing plants throughout the year. As we know, in winter, vegetables, berries and herbs are very expensive, so many summer residents build structures on their site with their own hands in order to always have fresh salads and compotes on the table. But before starting construction work, it is necessary to carefully think through the design of the future greenhouse, its heating system and make an accurate drawing.
Construction device
Today, winter greenhouses can be built from various materials. Therefore, each owner of a summer cottage can choose the most suitable and cost-effective options for himself.
Shapes and sizes of greenhouses:

The design of a winter greenhouse must withstand severe frosts, snowfalls and other atmospheric phenomena. The most durable, reliable and environmentally friendly material for constructing a greenhouse frame is wood. But such a structure can last no more than 15 years, and then it will have to be updated.
The most durable and profitable design is considered to be a greenhouse with polycarbonate cladding, since this material is of high quality, long service life and affordable price.
Any winter greenhouse must have a foundation, frame and glass roof. It is best to build such a structure from north to south. The room must have a good ventilation system to regulate heat and air conditions for the proper functioning of plants.
Ventilation can be supply or exhaust. The tightness of the greenhouse is the main condition for its effective functioning. The temperature is maintained artificially.
The greenhouse can be racked, in which the plants are placed on shelves with sides, or rackless, where the plants are planted directly into the ground. The racks in the greenhouse should be approximately at a height of about 60–80 cm from the ground, and the passage between them should be at least 70 cm. The racks are made of wooden boards, plastic or reinforced concrete, depending on the design features of the greenhouse.
Photo gallery: selection of project options
 Greenhouse drawing with dimensions
Greenhouse drawing with dimensions  Scheme of a rack greenhouse
Scheme of a rack greenhouse  Winter greenhouse design option
Winter greenhouse design option
Types of structures: advantages and disadvantages
Winter greenhouses come in several types depending on their design features, type of material used, type of lighting, heating system, and foundation design.
- Capital greenhouses are built on a strip foundation. A trench is dug in the center, which is designed to “collect” cold air, which should not reach the roots of the seedlings. Thanks to this design, the inside of the greenhouse warms up quickly enough and therefore seedlings can be planted several weeks earlier than usual.
- Capital types of conventional type greenhouses are collapsible structures that can be dismantled and moved around the site. To build such a greenhouse, a metal or plastic profile, polycarbonate, and bolted connections are used. Piles serve as the foundation.
The remaining types are prefabricated structures. Only in a permanent structure can a full-fledged heating and artificial lighting system be installed.
Greenhouses may differ in such parameters as:
- Functionality. They allow you to grow not only ordinary vegetables of a given region, but also exotic ones.
- Location in relation to the ground. There can be three types: recessed, surface and arranged in the upper part of a barn, garage, closet, etc.
- Architectural solution. They can be with a single-pitched, gable, three-pitched roof, as well as arched, wall-mounted and combined.
Greenhouses also differ:
- By type of building materials. They can be built from brick, wooden beams, metal profiles or PVC pipes. Polycarbonate or glass is used as a coating. Today, combined greenhouses, in which the walls are lined with polycarbonate and the roof is made of glass, are in great demand.
- According to the type of heating system. Winter greenhouses can operate on biofuel, solar panels, and also have stove, air, gas, water or electric heating.
- By type of planting seedlings and plants. They are planted in the ground or in specially knocked down boxes placed on shelves.
Depending on the design, greenhouses are divided into the following types:
- The thermos greenhouse, or as it is called the “Patia greenhouse,” despite the complexity of its design, is one of the most popular among summer residents. Its main part is located underground, due to which the “thermos” effect is achieved. It can also be above ground, but it must be covered from the inside with any heat-insulating material. In such a greenhouse, it is recommended to install a water heating system, as it will allow warm air flows to be evenly distributed throughout the room.
- A greenhouse with a gable roof is the most common design due to its convenience and versatility. The height of the greenhouse reaches 2-.5 meters to the ridge, so a person can walk in it without bending his head. Also, in it, seedlings can be grown not only on the ground, but also in special boxes on racks. The advantage of a gable design is that snow and rainwater do not accumulate on the roof surface, but quickly flow down. Disadvantages: high cost of materials, complexity of construction and large heat losses through the northern wall. Therefore, it must be additionally insulated with various heat-insulating materials.
- An arched greenhouse is considered a complex structure, as it often causes problems with the construction of the frame and cladding. Without a special device, it is almost impossible to bend metal pipes to make a frame (but you can take PVC pipes). It is not possible to use glass to cover the frame, so all that remains is polycarbonate or various types of greenhouse films. The disadvantage of an arched greenhouse is the real danger of cracks in the polycarbonate during heavy snowfall, since if the layer is too large, the roof will not withstand the load. There is no possibility to place racks and shelves inside such a structure, so plants can only be grown on the ground.
- Greenhouse with sloping walls. The design of such a greenhouse resembles an ordinary “house” in appearance, but only with walls built at a certain angle, extending outside the room. The advantage of such a greenhouse is the possibility of construction from wood, metal, and plastic. Glass, polycarbonate, film can serve as cladding. The biggest advantage is considered to be a “self-cleaning” gable roof. The downside is the restrictions on installing racks and shelves around the perimeter of the walls due to the sloping walls.
- Greenhouse with mansard roof. A type of structure with vertical walls and a mansard roof, which copes well with mechanical loads such as snow. Thanks to the special roof, more space is created above your head, and a large number of multi-tiered racks and shelves can be placed on the walls.
- Single slope greenhouse. The design of the walls is no different from a gable roof, but here the roof is installed at a certain angle so that snow falls off it and rainwater drains without getting inside the room. Glass and polycarbonate can be used for cladding. Polyethylene film is not suitable for a winter greenhouse. Along the walls you can install shelves and racks on top of each other for multi-tiered growing of plants. It is practically devoid of disadvantages, except for the complexity of construction and installation of a strip foundation.
Preparatory work: drawings and dimensions of the structure
We will consider the construction of a winter greenhouse 3.34 meters wide and 4.05 meters long. The total area of the room for growing crops is 10 square meters. meters.
The greenhouse is a square room buried in the ground with shelves and a roof made of durable two-layer polycarbonate.
If there is groundwater on the site and it is close to the surface, then the greenhouse is built without deepening, and the outer sides of the structure are sprinkled with soil.
If necessary, the length of the structure can be increased by adding additional sections to the frame.
Structure of racks and their dimensions
Where the beam connects, a triangular-shaped support is built. The dimensions are shown below in the drawing.
Ridge posts are needed to support the timber at the connection point. Also, the support should not come into contact with the polycarbonate sheathing.
A strong support system will not interfere when a person moves around the greenhouse. It is necessary if the length of the greenhouse is more than 4 meters. If the length exceeds these parameters, then supports are installed every 4 meters.
Corner supports are made of 100x100 mm timber, intermediate supports are made of 50x100 mm boards.
Construction of walls and thermal insulation
The pillars will be covered with boards on both sides, and insulation will be placed in the interior space.
To save money, you can take round timber Ø 120–150 mm, hewn to 100 mm. The walls are covered with slabs.
To insulate walls, use slag, sawdust or fine expanded clay. Quicklime is added to sawdust as protection against small rodents.
When choosing timber and boards, it is necessary to take into account that this structure will be used throughout the year, so the lumber must be of high quality.
- For the construction of supports and other parts of the frame, it is recommended to purchase pine boards and timber (rounded or glued). This is the most accessible, durable and cost-effective material for the construction of greenhouses in our region.
You can also choose larch or oak, but such lumber is quite expensive and therefore it is irrational to use them in this case.
Polycarbonate has excellent heat and sound insulation characteristics. But the more complex its structure, the greater the mechanical loads it can withstand (snow and wind).
When choosing polycarbonate, you need to know its thickness.
- For cladding the walls of a greenhouse, it is best to take sheets with a thickness of 6 to 25 mm, depending on the intended design.
- For roofing, polycarbonate with a thickness of 16 to 32 mm is recommended, since this part of the greenhouse will bear the heaviest load.
Calculation of the required amount of material and tools
- Beam with a section of 100x100 mm;
- Board with a section of 50x100 mm;
- Gorbyl;
- Round timber Ø 120–150 mm;
- Boards for making shelving;
- Insulation;
- Foamed polyethylene (aluminum foil);
- Polycarbonate sheets;
- Self-tapping screws and thermal washers;
- Hardware;
- Screwdriver;
- Wood hacksaw or saw;
Step-by-step instructions for building an in-depth winter greenhouse with your own hands
We dig a pit 60 cm deep. Its length and width should be several centimeters larger than the perimeter of the future greenhouse. At the bottom we make markings for installing support pillars. We dig in the supports to a depth of about 50 cm.
At a height of one meter from the ground, stretch the construction rope and check the evenness using a level. We fill the supports with soil and compact them thoroughly.
We level the floor and cover the walls with boards outside and inside, starting from the bottom. We fill the space between them with the selected insulation. This is how we cover the opposite two walls.
After we have sheathed the walls, we need to saw off the excess ends of the boards that extend beyond the pillars. At the corners of the structure inside, we nail 50x50 mm bars onto the boards. Next, we will attach the sheathing to them on the front and back of the wall. This is how we sew up all the walls of the greenhouse. But we nail the boards to the vertical beams.
We compact the insulation inside the walls, adding the required amount of expanded clay, sawdust or slag to the top. Then we sew up the top of the walls with boards.
We also cover the inner surface of the walls with insulation made from special foil. We place the insulation so that it extends slightly at the top of the walls, and bend it so that it can cover the boards covering the upper part of the walls.
We make the roof separately from the main structure, and then install it on the greenhouse. We manufacture all other roofing elements according to the diagrams indicated in the drawing.
We connect the rafter parts into half a tree, and nail the lintel so that the distance at the bottom is 3 meters 45 centimeters. Since the jumper is temporary, we must nail it so that it can then be dismantled. The nails should not be driven in completely, but should be left 10 mm from the head so that they can be easily removed.
We assemble the rafters and nail them to the support as shown in the drawing below.
After we have nailed the rafters to the support, we remove the jumpers. We install the ridge beam under the rafters and place the front posts measuring 88 cm under it. We nail the outer rafters (20 cm) to the ridge beam. To do this, we pre-drill holes in the rafters. Then we install a jumper between the rafters, and install flashings on the side rafters, the ridge beam and on the front posts as shown in the drawing.
Reference. Strips are called wooden strips that are designed to cover various cracks.
We attach two-layer thick polycarbonate to the roof frame using self-tapping screws with thermal washers. To do this, we drill holes in the sheets larger than the diameter of the screws themselves.
After attaching the polycarbonate, we need to install a ridge corner from galvanized sheet metal. We fasten it with a gasket for insulation. We do not attach polycarbonate to the side ends of the roof until we have secured the roof to the main structure.
We install the roof on the walls and secure it with 4 metal brackets. They can be made from twenty-centimeter long nails. Then we install the side parts of the roof from polycarbonate triangles.
We install an insulated thick wooden door (thickness at least 5 cm).
After this, you can install wooden racks and shelves inside the greenhouse for future seedlings. They are installed on the sides of the walls at a distance of approximately 60 cm from the floor. A layer of earth is poured on them or boxes with soil are placed.
Heating selection
The choice of heating system depends on the size of the room. For winter greenhouses with an area of more than 15 square meters. meters, stove heating is suitable. Large areas are usually heated with biofuel, electric heaters or a water loop.
Stove heating is an affordable and economical option for a greenhouse. In this case, a stove is installed in the room, which is heated with wood, coal, briquettes, pallets or gas. But since the walls of the oven become very hot, plants should not be planted near it.
Water heating requires a water heating boiler, pipes and a tank. The pipes are buried in the ground to a depth of about 40 cm or placed immediately under the shelves.
Electric heating can be of three types: air, cable and infrared. Cable is a “warm floor” system, air is installed using fan heaters, and infrared is produced by special heating devices that are mounted under the roof of the greenhouse.
Biofuel heating is the most cost-effective heating option. Here, the indoor air is warmed due to the heat generated during the decomposition of various organic substances.
The most used biomaterials are:
- Horse manure - capable of maintaining a temperature of 33 to 38°C for 2–3 months;
- Cow dung - can keep 20°C for about 3.5 months;
- Rotted tree bark - keeps at 25°C for about 4 months;
- Sawdust - maintain 20°C for only 2 weeks;
- Straw - can maintain a temperature of 45°C for up to 10 days.
Biofuel is placed in the ground under the top layer of fertile soil. When choosing a fuel type, it is necessary to take into account its acidity level, since it significantly affects the quality of the soil. Cow dung is considered the best as its acidity level is 6-7 pH. A more acidic environment is created by bark and sawdust, and an alkaline environment is created by horse manure. Biofuel after its use can be reused as humus.
The type of heating is selected individually for each specific case, based on parameters such as the climate of the region, planned expenses and type of plants.
- Before starting construction of the greenhouse, all wooden boards and beams must be treated with antifungal and antiseptic agents.
- Before installing the supports, after treating them with protective agents, the lower parts must be tightly wrapped with roofing material and secured with a stapler.
- It is also necessary to protect the external walls by securing roofing felt to them. And only then sprinkle them with soil.
- The roof frame, after applying a protective coating and primer, is covered with white paint intended for outdoor work.
- During the operation of the greenhouse, it is necessary to choose energy-saving lamps to create artificial lighting. They help you use electricity more economically. Their number and location depend on the dimensions of the internal space of the greenhouse.
Video: how to build a winter greenhouse with your own hands
If, when constructing a winter greenhouse, you strictly observe all technical standards and follow the drawn up diagrams and drawings, then such a design will delight you and your loved ones with excellent harvests of vegetables, berries and fresh herbs for decades.
For a person who is passionate about growing his own vegetables and fruits, having a greenhouse on his property is not a novelty. But not all greenhouses are the same - some are needed for growing seedlings and early forcing of the first greens, others are designed to produce several harvests per season. And winter greenhouses are considered aerobatics. After all, growing garden crops all year round is a complex and energy-consuming task, requiring not only agronomic knowledge, but also serious technical training.
A properly equipped greenhouse maintains an optimal microclimate even in severe frosts
In order to correctly design and calculate all the nuances of building a winter greenhouse, you need to understand that you will have to do more than just slightly adjust the weather conditions. It is necessary to recreate optimal lighting practically from scratch, ensure comfortable temperature and humidity, control watering and gas exchange - and all this in conditions of low temperatures, deep freezing of the soil, strong winds and insufficient sunlight.
When planning construction, special attention should be paid to the following:
- type of greenhouse;
- placement and dimensions of the structure;
- Construction Materials;
- foundation pit depth;
- heating and lighting systems;
- water supply and ventilation.
The project also necessarily takes into account the climatic region in which construction is planned, the specific agricultural technology of the planned crops and the costs of constructing and maintaining the pavilion.
What buildings are suitable for a winter garden?

It is important to choose a durable frame
There are many design options for a winter greenhouse. This is not surprising - relatively light structures are suitable for the southern regions, but in the central and northern regions such a shelter usually looks like a permanent building with a deep foundation, a high base and a solid roof. The type is determined by several parameters:
- Location. There are three options - deep into the ground, above ground and superstructures (winter gardens and greenhouses in attics).
- Heating. According to the type of heating, greenhouses are equipped with biofuel, technical heating and solar heating (solar greenhouses).
- Architecture. Here everything is limited only by the designer’s imagination - single- and double-slope, geodesic, arched, wall-mounted. The main thing is that the design retains heat well and is comfortable to work in.
- Functionality. The choice of building materials (wood, brick, glass, film, polycarbonate), the internal arrangement system and the types of beds depend on what you plan to grow.
Stages and nuances of construction
Many summer residents, having thought about how to build a winter greenhouse on their site, come to the conclusion that it is very difficult and unprofitable. In fact, everything is not quite like that - yes, the construction of such a structure requires significant investments, but even a not very experienced master can do it.
The main thing is to design the structure correctly, think through the nuances of the location and select high-quality materials.
The best projects for country house construction
According to many gardeners, four types of greenhouses are most convenient for home construction:
- winter shelter with earthen filling:
- greenhouse with double film covering;
- wall-mounted lean-to building;
- gable winter greenhouse.

It is easier to maintain optimal temperature in an underground shelter at a depth of 2.5 m

In the southern regions, the frame can be sheathed with two layers of film

Single-slope wall-mounted above-ground greenhouse

Gable glass greenhouse
Which type to choose depends on the specific climatic conditions and characteristics of the selected heating system.
Bioheating is more suitable for a recessed greenhouse with earthen filling. And it is more profitable to install steam heating in a wall-mounted structure - if the greenhouse is built near the house, then the pipes are simply connected to the main heating system.
It is also necessary to think about how to make the winter greenhouse illuminated, since in winter there is not enough sunlight, especially in recessed structures.
When installing artificial lighting, it is better to combine several types of lamps (incandescent, fluorescent, mercury, LED) - this makes it more convenient to choose the mode and spectrum of lighting.

Automatic infrared heating system
Preparing the installation site
To build a winter greenhouse with your own hands, you need to decide on the type of structure and, based on its characteristics, select a site and prepare the soil. If this is not a wall-mounted pavilion, then for construction you should choose an open area on a small hill. If there is no such place, then you should pay attention to the location of the nearest trees or buildings - they should be located on the leeward side at a distance of about 8 meters from the building. This will protect the structure from winds and ensure maximum illumination of the walls and roof of the shelter.

Foundation for a ground-based winter greenhouse
The depth of the pit depends on the type - for in-depth structures, the pit is dug one and a half meters below the soil freezing level. For above-ground shelters, the foundation pouring depth is only about half a meter, since a high base is erected to protect the beds.

Sectional diagram of the foundation
Features of the construction of ground structures
In an above-ground greenhouse for winter, it is very important to protect the beds from freezing. Therefore, one of the features of such a structure is a double plinth of at least a meter in height. The material for its construction can be brick, natural stone, adobe (for the internal wall). It is advisable to fill the gap between the outer and inner basement walls with insulation - expanded clay, mineral wool or other available material.
What material to choose for the frame
To build the frame of a winter greenhouse, you can use a wooden beam or a metal profile. The main condition is that the racks must be strong, since in winter the load on the support beams increases due to snow cover.
- The metal profile is strong and durable, but inconvenient to use and expensive.
- A modern metal-plastic frame is much easier to install, but it may not be strong enough to withstand the load of snow cover
- A wooden frame will cost less, it is convenient to install and sheathe. Before assembly, wooden parts must be impregnated with an antifungal compound and painted.
When installing the frame, be sure to install several windows to ventilate the room.

Finished wooden frame

Reinforced metal frame

Factory greenhouse under polycarbonate
How to cover the frame
To cover the frame, use cellular polycarbonate with a thickness of at least 16 mm, double-glazed windows or film (suitable for southern regions). Today, a winter greenhouse made of polycarbonate is considered the most profitable - it is strong and durable, retains heat well and lets in enough sunlight; if necessary, damaged sheets are easy to replace.

Cellular polycarbonate is an ideal material for cladding
Glass for winter pavilions is not the best choice. Its main drawback is its fragility, so when using this material for cladding, the roof must be sloped with a slope of more than 45°, this way it will be possible to avoid the accumulation of snow and damage to the roof.
A good option for beginners is covering it with greenhouse film in two layers, with a gap of at least 10 cm (the film is attached outside and inside the frame). For the roof, use dense air bubble film laid in 3 layers. But this method is good for warm climates, where the temperature in winter does not drop below 10 °C.
Important! It is imperative to seal all seams and joints in the sheathing - this will avoid heat loss and drafts.
Which heating system to choose

Water heating installation diagram
When choosing heating for a winter greenhouse, you should focus on the area, the cost of energy and the efficiency of the method. For a small room it is better to choose the following options:
- “warm floor” heating (evenly warms the air in the room and protects the soil from freezing);
- electric heating with convectors or heaters;
- water heating (it is better to lay pipes under the beds and along the walls, and connect the system to a home heating boiler);
- infrared heaters (economical and harmless method);
- wood or air heating (requires constant monitoring and significant fuel consumption);
- bioheating (manure or compost is placed under the beds, suitable for deep greenhouses).

Electrical soil heating
Advice! When using electric heaters, it is better to install them under shelving - this way the seedlings will not be exposed to the flow of hot air.
In order to keep the room warm even in case of unforeseen situations, it is necessary to install backup heating systems. These can be combined “gas-wood” or “gas-electricity” boilers, barrels of water or a stove (iron or brick) right in the pavilion with beds.
Sprinkler systems are installed for irrigation in winter greenhouses, since soil drip irrigation can lead to the death of plants if the beds are not protected from freezing.
Construction of a gable greenhouse for a personal plot

Scheme of a recessed gable greenhouse
This polycarbonate winter greenhouse project has proven itself well both in the middle zone and in areas with cold climates. The length and width are selected individually, but for a summer residence an area of 20-25 square meters is considered optimal. m. The structure consists of a utility block and a greenhouse. It is better to use a wooden beam for the frame; the structure is sheathed with polycarbonate. Experts advise paying attention to the following points:
- The pit is dug depending on the depth of soil freezing by 1-1.5 meters.
- The foundation is poured strip: 40x40 cm or 50x50 cm.
- The walls inside the pit and the base at a height of 50 cm are laid in one brick.
- A frame is mounted on the base, which is sheathed with 10-16 mm cellular polycarbonate.
- Ventilation vents are installed on the walls and roof.
- The northern wall can be made blank; it is better to line it inside with reflective material.
- In the vestibule of the greenhouse, a boiler or furnace is installed for heating, and lighting and irrigation control units are installed.
- The partition between the pavilion and the utility block can be made transparent (double-glazed windows) or solid.
If capital construction is not yet affordable, but you still want to try growing vegetables in winter, you can try the economical option of bioheating with film covering. You can see how to quickly make a winter greenhouse with your own hands in the film.
As you can see, building a greenhouse in which you can grow vegetables all year round is troublesome, but quite possible. The main thing is to calculate everything accurately and make sure that the costs of constructing a winter pavilion are fully justified.
Latest site materials
Online services
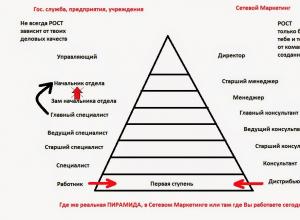
The naked truth about NL International
Network business is popular on the Internet. Many claim that such a business allows you to earn millions. Network" or "MLM business" got its name from MLM - Multi-Level-Marketing (translated from English - multi-level marketing). This is aimed
Calculation

Handmade Soap Making Business as a Business Handmade Soap Making Business
Working from home is a very real business for those who want to work at home, without large investments and solely through their labor and creativity. The cost of purchasing materials and equipment is not all that is needed. First you need to study the specifics
Calculation

What is the difference between a franchise and franchising?
McDonalds, Subway, Orange Elephant, Zara, Sbarro, Shokoladnitsa - what unites all these famous brands? The fact that franchising helped them all achieve wild popularity. By the way, even the Russian fuel giant Lukoil is selling its franchise. However, many
Control

How to make money on the stock exchange: examples Ways to make money on the stock exchange
— How to make your first money in the market — What should a beginner know? — 3 successful strategies for trading on exchanges — Useful tips — 5 fatal mistakes in playing the markets — Two main ways to make money on trading platforms — 8 mandatory steps for beginners in trading
Acts

Themes for business without investment
Many people who decide to open their own business cannot immediately count on a large sum to create investments. Don’t despair - a business with minimal costs will come to the rescue. Using inexpensive but profitable business ideas at minimal cost
Registration
Rabbit farming is a profitable business
Livestock farming is considered one of the most complex, resource-intensive and at the same time profitable areas of agriculture. However, this type of business is not necessarily characterized by multimillion-dollar investments in the purchase or construction of huge farms. K p